Atlantic slave trade american colonies
The origins of slavery in the colonial United States — are complex and there are several theories that have been proposed to explain the trade. It was largely tied to European colonies' need for labor, especially plantation agricultural labor in their Caribbean sugar colonies operated by Great BritainFranceSpainand the Dutch Republic.
Most slaves who were brought or kidnapped to the Thirteen British colonies which later became the Eastern seaboard of the United States were imported from the Caribbeannot directly from Africa. They arrived in the Caribbean predominantly as a result of the Atlantic slave trade. Indigenous people were also enslaved in the North American colonies, but on a much smaller scale. Slave status for Africans usually became hereditary. While they knew about Spanish and Portuguese slave trading, the British did not implement slave labor in the Americas until the 17th century.
The first Africans to arrive in England came voluntarily with John Lok an ancestor of the famous philosopher John Locke in Lok intended to teach them English in order to facilitate trading of material goods. InEngland established Jamestown as its first permanent colony on the North American continent. Once it became clear that tobacco was going to drive the Jamestown colony, more labor was needed.
The British aristocracy needed to find a labor force to work on its plantations in the Americas. The major possibilities were indentured servants from Britain, Native Americans, and West Africans. These and other Caribbean colonies became the center of wealth and the focus of the slave trade for the growing English empire. Towards indigenous Americans, the English entertained two lines of thought simultaneously.
Because these people were lighter skinned, they were seen as more European and therefore as candidates for civilization. At the same time, because they were occupying the land desired by the colonial powers, they were from the beginning, targets of a potential military attack.
At first, indentured servants were used as the needed labor. Once the seven years was over, the indentured servant was free to live in Jamestown as a regular citizen.
However, colonists began to see indentured servants as too costly, and inDutch traders brought the first African slaves to Jamestown, who nonetheless were in North America at first generally treated as indentured servants. Several Colonial colleges held enslaved people and relied on captives to operate. Until the early 18th century, enslaved Africans were difficult to acquire in the colonies that became the United States, as most were sold in the West Indies.
One of the first major establishments of African slavery in these colonies occurred with the founding of Charles Town and the Province of Carolina in The colony was founded mainly by planters from the overpopulated British sugar island colony of Barbadoswho brought relatively large numbers of African slaves from that island. For several decades it was difficult to acquire African slaves north of the Caribbean. To meet agricultural labor needs, colonists practiced Indian slavery for some time.
The Carolinians transformed the Indian slave trade during the late 17th and early 18th centuries by treating slaves as a trade commodity to be exported, mainly to the West Indies. Alan Gallay estimates that between andbetween 24, and 51, captive Native Americans were exported from South Carolina—much more than the number of Africans imported to the colonies of the future United States during the same period.
The first Africans to be brought to British North America landed in Virginia in They arrived on a Dutch ship that had captured them from the Spanish.
These approximately 20 individuals appear to have been treated as indentured servantsand a significant number of enslaved Africans even won their freedom through fulfilling a work contract or for converting to Christianity.
To many historians, notably Edmund Morganthis evidence suggests that racial attitudes were much more flexible in 17th century Virginia than they would later become. In there wereand in there were Slaves, African and indigenous, were a smaller part of the New England economy and a smaller fraction of the population, but they were present.
Colonists came to equate this term with Native Americans and Africans. The Dutch West India Company introduced slavery in with the importation of eleven enslaved blacks who worked as farmers, fur traders, and builders to New Amsterdam present day New York Citycapital of the nascent province of New Netherland[25] which later expanded across the North River Hudson River to Bergen in today's New Jersey. Later slaves were held privately by the settlers to the area. Admitted to the Dutch Reformed Church and married by its ministers, their children could be baptized.
Slaves could testify in court, sign legal documents, and bring civil actions against whites. Some were permitted to work after hours earning wages equal to those paid to white workers.
When the colony fell to the English in the s, the company freed all its slaves, establishing early on a nucleus of free negros. Enslaved Africans performed a wide variety of skilled and unskilled jobs, mostly in the burgeoning port city and surrounding agricultural areas.
The French introduced legalized slavery into their colonies in New France near the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River. After the port of New Orleansto the south, was founded inmore African slaves were imported to the Illinois Country for use as agricultural or mining laborers. By the mid-eighteenth century, slaves accounted for as many as a third of the population in that area. The first people enslaved by the French were Native Americans. Africans were brought to the area in the early 18th century, as part of efforts to develop the colony.
Implemented in colonial Louisiana inLouis XIV of France 's Code Noir regulated the slave trade and the institution of slavery in the French colonies.
It gave Louisiana a very different pattern of slavery compared to the rest of the United States. Although it authorized and codified cruel corporal punishment against slaves under certain conditions, it forbade slave owners to torture them or to separate married couples or to separate young children from their mothers.
It also required the owners to instruct slaves in the Catholic faith, implying that Africans were human beings endowed with a soul, an idea that had not been acknowledged until then. The Code Noir also forbade interracial marriages, but interracial relationships were formed in New Orleans society. The mulattoes became an intermediate social caste between the whites and the blacks, while in the English colonies the mulattoes and blacks were considered equal and discriminated against equally.
The Spanish introduced slavery in Florida soon after they claimed it in Spanish settlement was sparse and there were comparatively few slaves. The barriers of slavery hardened in the Second half of the 17th century, and imported Africans' prospects grew increasingly dim.
Bythe Virginia courts had sentenced at least one black servant, John Punchto slavery. In the Virginia House of Burgesses passed a law with the doctrine of partusstating that any child born in the colony would follow the status of its mother, bond or free. This was an overturn of a longheld principle of English Common Lawwhereby a child's status followed that of the father. It enabled slaveholders and other white men to hide the mixed-race children born of their rape of slave women and removed their responsibility to acknowledge, support, or emancipate the children.
During the second half of the 17th century, the British economy improved and the supply of British indentured servants declined, as poor Britons had better economic opportunities at home. At the same time, Bacon's Rebellion of led planters to worry about the prospective dangers of creating a large class of restless, landless, and relatively poor white men most of them former indentured servants.
Wealthy Virginia and Maryland planters began to buy slaves in preference to indentured servants during the s and s, and poorer planters followed suit by etrade price type options. Slaves cost more than servants, so initially only the wealthy could invest in slaves.
Atlantic slave trade american colonies first British colonists in Carolina introduced African slavery into the colony inthe year the colony was founded, and Charleston ultimately became the busiest slave port in North America. Slavery spread from the South Carolina Lowcountry first to Georgia, then across the Deep South as Virginia's influence had crossed the Appalachians to Kentucky and Tennessee.
Northerners also purchased slaves, though on a much smaller scale. Enslaved people outnumbered free whites in South Carolina from the early s to the Civil War. An authoritarian political culture evolved to prevent slave rebellion and justify white slave holding. Northern slaves typically dwelled in towns, rather than on plantations as in the South, and worked as artisans and artisans' assistants, sailors and longshoremen, and domestic servants.
InKing Charles II rechartered the Royal African Company it had initially been set up inas an English monopoly for the African slave and commodities trade—thereafter inby statute, the English parliament opened the trade to all English subjects.
The North American royal colonies not only seminar stock trading Africans but also captured Native Americans, impressing them into slavery. Many Native Americans were shipped as slaves to the Caribbean. Many of these slaves from the British colonies were able to escape by heading south, to the Spanish colony of Florida. There they were given their freedom, if they declared their allegiance to the King of Spain and accepted the Catholic Church.
In Fort Mose was established by African American freedmen and became the northern defense post for St. InEnglish forces attacked and destroyed the fort, which was rebuilt in Because Fort Mose became a haven for escaped slaves from the English colonies to the north, it is considered 100 win binary options virtual account precursor site of the Underground Railroad.
Curiously, chattel slavery developed in British North America before the legal apparatus that supported slavery did. During the late 17th century and early 18th century, harsh new slave codes limited the rights of African slaves and cut off their avenues to freedom. The first full-scale slave code in British North America was South Carolina'swhich was modeled on the colonial Barbados slave code of and was updated and expanded regularly throughout the 18th century.
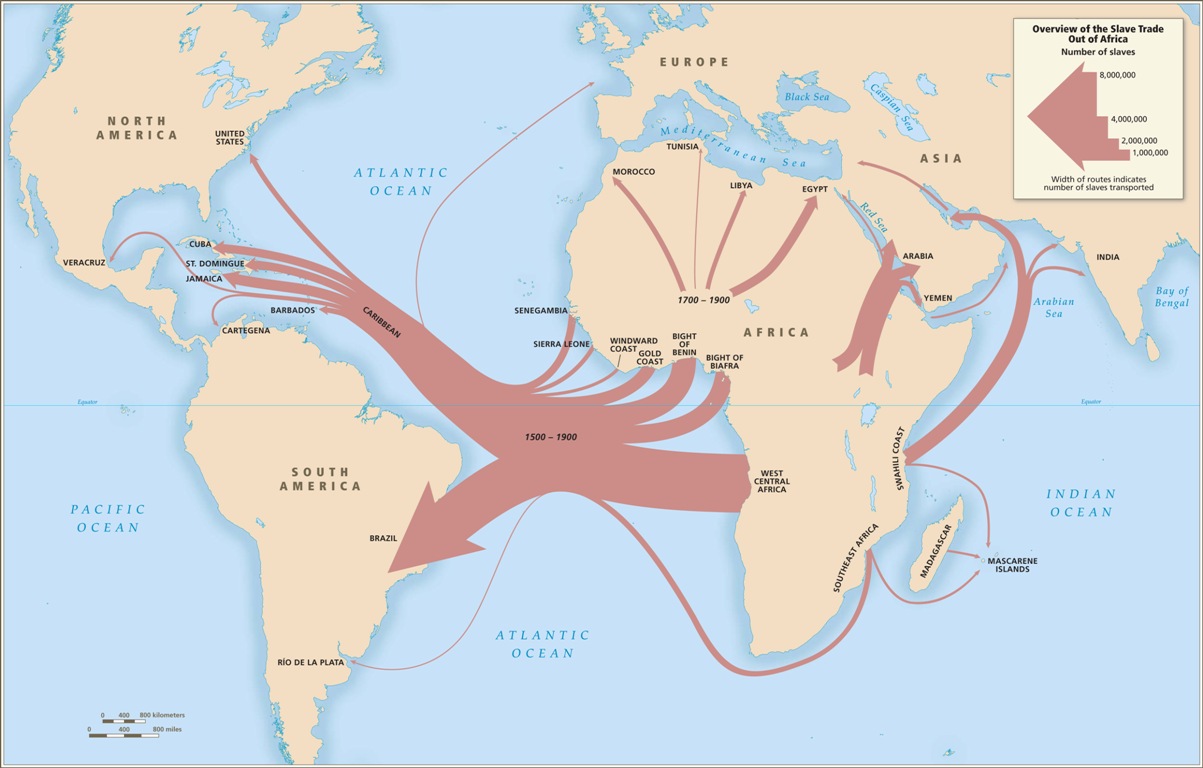
A Virginia law prohibited slaveholders from emancipating slaves unless they paid for the freedmen's transportation out of Virginia. The vast majority of slaves transported across the Atlantic Ocean were sent to the Caribbean sugar colonies, Brazilor Spanish America. Throughout the Americas, but especially in the Caribbean, tropical disease took a large toll on their population and required large numbers of replacements. Many Africans had a limited natural immunity to yellow fever and malaria ; but malnutrition, poor housing, inadequate clothing allowances, and overwork contributed to a high mortality rate.
In British North America the slave population rapidly increased via the birth rate, whereas in the Caribbean empire stockbroker series 65 they did not. The lack of proper nourishment, being suppressed sexually, and poor health are possible reasons. It was not only the major colonial powers of Western Europe such as FranceEnglandSpainPortugaland the Netherlands that were involved.
Other countries, including Sweden and Denmark, participated in the trans- Atlantic slave trade though on a much more limited scale. They would atlantic slave trade american colonies sent out on errands, but in most cases their jobs required that they spend much of forex online trading seminar cd time within their owner's household.
In Southern colonies and smaller farms, however, women and men typically engaged in the same roles, both working in the tobacco crop fields for example. Although slave women and men in some areas performed the same type of day-to-day work, "[t]he female slave Slave owners saw slave women in terms of prospective fertility. That way, the number of slaves on a plantation could multiply without having to purchase another African.

Unlike the patriarchal society of white Anglo-American colonists, "slave families" were more matriarchal in practice. Men, in turn, were often separated from their families. Some historians, notably Edmund Apa itu trading dan forex, have suggested that indentured servitude provided a model for slavery in 17th-century Virginia.
In practice, indentured servants were teenagers in England whose father sold their labor voluntarily for a period of time typically four to seven yearsin return for free passage to the colonies, room and board and clothes, and training in an occupation.
Pre-contact indigenous peoples in the American southeast had practiced a form of slavery on people captured during warfare. Larger societies structured as chiefdoms kept slaves as unpaid field laborers, while in band societies the ownership of enslaved captives attested to their captor's military prowess.
Richard Whitein The Middle Ground elucidates the complex social relationships between American Indian groups and the early empires, including 'slave' culture and scalping. It was a new kind of slaving, requiring top earning options traders new kind of occupational specialty…organized militaristic slavers. In Junethe Virginia assembly granted Bacon and his men what equated to a slave-hunting license by providing that any enemy Indians caught were to be slaves for life.
They also provided soldiers who had captured Indians with the right to "reteyne and keepe all such Indian slaves or other Indian goods as they either have taken or hereafter shall take. In the years to follow, other laws resulted in Indians being grouped with other non-Christian servants who had forex scalper ea forum to the colonies Negro slaves as slaves for life.
Puritan New England, Virginia, Spanish Florida, and the Carolina colonies engaged large-scale enslavement of Native Americans, often through the use of Indian proxies to wage war and acquire the slaves.
In New England, slave raiding accompanied the Pequot War and King Philip's War, but declined after the latter war ended in Enslaved Indians were in Jamestown from the early years of the settlement, but large-scale cooperation between English slavers and the Westo and Occaneechi peoples, whom they armed with guns, did not begin until the s. These groups conducted enslaving raids in what is now Georgia, Tennessee, North Carolina, South Carolina, Florida, and possible Alabama. Historian Ulrich Phillips argues that Africans were inculcated as slaves and the best answer to the labor shortage in the New World because American Indian slaves were more familiar with the environment, and would often successfully escape into the wilderness that African slaves had much more difficulty surviving in.
Also, early colonial America depended heavily on the sugar tradewhich led to malariaa disease the Africans were far less susceptible to than Native American slaves. Colonial slave rebellions beforeor before for Louisiana include:. Until recently, the only known racial groups in the colonies were Native Americans, the African slaves and the white colonists.
Recent research, however, has shown that small numbers of East Indians were brought over to the colonies as enslaved laborers, as both India and the colonies were under British control.
Conversion rate chf to usd Virginia Gazette of Aug. Today, descendants of these Indian slaves have a very small percent of DNA from their Asiatic ancestors, how do you make money bartering most of their ancestry is African. African and African American slaves expressed their opposition to slavery through armed uprisings such as the Stono Rebellion and the New York Slave Insurrection ofthrough malingering and tool-breaking, and most commonly, by running away, either for short periods or permanently.
Until the Revolutionary era, almost no white American colonists spoke out against slavery. Even the Quakers generally tolerated slaveholding and slave-trading until the midth century, although they emerged as vocal opponents of slavery in the Revolutionary era.
Infour German Quakers in Germantowna town outside Philadelphiawrote a petition against the use of slaves by the English colonists in the nearby countryside. They presented the petition to their local Quaker Meeting, and the Meeting was sympathetic, but could not decide what the appropriate response should be. The Meeting passed the petition up the chain of authority to Philadelphia Yearly Meetingwhere it continued to be ignored and was archived and forgotten for years. In the petition was rediscovered and became a focus of the burgeoning abolitionist movement.
It was the first public American document of its kind to protest slavery. It was also one of the first public declarations of universal human rights. Thus although the petition itself was forgotten, the idea that every human has equal rights was discussed in Philadelphia Quaker society over the next century. Slavery was officially sanctioned by Philadelphia Yearly Meeting in Following the Revolution, the northern states all abolished slavery, with New Jersey acting last inalthough some of these laws merely reclassified slaves as indentured servants effectively maintaining slavery by another name.
Acting on the advice of President Thomas Jeffersonwho denounced the international trade as "violations of human rights which have been so long continued on the unoffending inhabitants of Africa, in which the morality, the reputation, and the best interests of our country have long been eager to proscribe" in Congress banned the international slave trade. However, the domestic slave trade continued.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. This article is about slavery in the Colonial era. For slavery after the United States were formed, see Slavery in the United States. Child labour Conscription Debt Forced marriage Bride buying Wife selling Forced prostitution Human trafficking Peonage Penal labour Sexual slavery. By country or region. Sub-Saharan Africa Contemporary Africa Slavery on the Barbary Coast Barbary slave trade Slave Coast Angola Chad Ethiopia Mali Mauritania Niger Somalia South Africa Sudan Seychelles North and South America Americas indigenous U.
Anti-Slavery International Blockade of Africa U. Compensated emancipation Freedman manumission Freedom suit Abolitionists Slave Power Underground Railroad songs Slave rebellion Slave Trade Acts International law 13th Amendment to the United States Constitution.
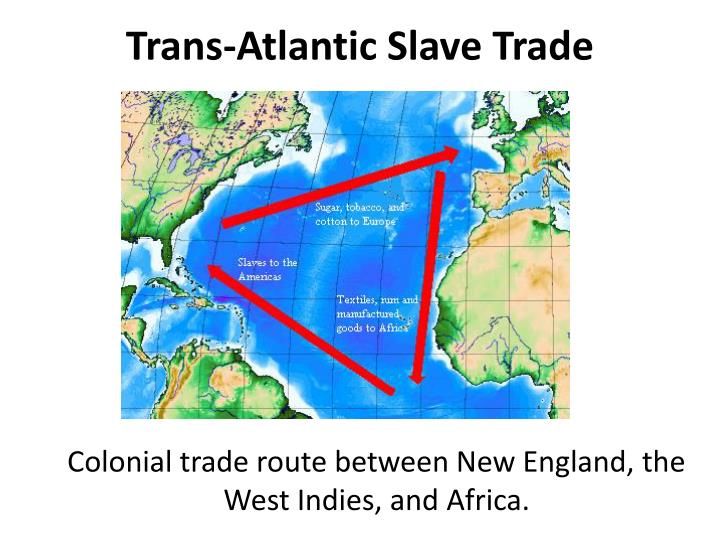
Triangle Trade (Rum and Slave Trade) - Definition
Common law Indentured servant Unfree labour Fugitive slaves laws Great Dismal Swamp maroons List of slaves owners Slave narrative films songs Slave name Slave catcher Slave patrol Slave Route Project Treatment in U.
Indentured servitude in the AmericasRedemptionerand Indian slave trade in the American Southeast. Slavery at common law and Atlantic slave trade. Colonial period of South Carolina. History of slavery in Virginia and History of slavery in Maryland.
Atlantic slave trade - Wikipedia
History of slavery in New York and History of slavery in New Jersey. Slavery in New France. History of slavery in Florida. Slavery among Native Americans in the United States. Abolitionism in the United States. Colonial history of the United States Free negro Grand Model for the Province of Carolina History of slavery in Connecticut History of slavery in Georgia History of slavery in Maryland History of slavery in Massachusetts History of slavery in New Jersey History of slavery in New York History of slavery in Pennsylvania History of slavery in Rhode Island History of slavery in Virginia Indentured servitude in the Americas Redemptioner Indentured servitude in Pennsylvania Indentured servitude in Virginia Slave Trade Act Slavery among Native Americans in the United States Indian slave trade in the American Southeast Slavery at common law Slavery in the British and French Caribbean Slavery in the Spanish New World colonies.
Ira Berlin, Generations of Captivity: A History of African-American Slaves Indeed, West Africans scarcely figured at all in the sixteenth-century English agenda for the New World.
The Roots of African Slave Trade: who started it, and who stopped it (Documentary)The negative connotations that the English had long attached to the color black were to deeply prejudice their assessment of West Africans. The men in question had come to England willingly. Lok's sole motive was to facilitate English trading links with West Africa. He intended that these five men should be taught English, and something about English commercial practices, and then returned home to act as intermediaries between the English and their prospective West African trading partners.
E2BN - East of England Broadband Network and MLA East of England. Retrieved 28 June Race, Slavery, and the Troubled History of America's Universities. The Rise of the English Empire in the American South — ISBNpg. Morgan, American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia New York: Norton,pp. In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process: The William and Mary Quarterly: African Americans in New York and East Jersey,Chapel Hill, North Carolina: Jersey City Past and Present.
New Jersey City University. French Roots in the Illinois Country. University of Illinois Press. Steinberg, "Disorders of Hemoglobin: Genetics, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Management", pp. How Monotheism Led to Reformations, Science, Witch-hunts, and the End of Slavery", p. Jones, "The Louisiana Journey", p. The Ashley Cooper Plan: The Founding of Carolina and the Origins of Southern Political Culture. University of North Carolina Press, Chapters 1 and 4. Viking,p.
These laws would be modified and added to over the next century and a half, but the essential legal framework within which the institution of slavery would subsequently operate had been put in place.
Slavery in Colonial America. Men, Women, and Gender". Retrieved December 2, In Joy and In Sorrow: Women, Family and Marriage in the Victorian South.
ISBNp. Indians, Empires, and Republics in the Great Lakes Region. American Slavery, American Freedom. Abraham Lincoln and American Slavery.
Second Term, pp. History of the United States. Prehistory Pre-Columbian Colonial —89 — —65 — —45 —64 —80 —91 — —present. American Century Cities Constitution Demographic Diplomatic Economic Education Immigration Medical Merchant Marine Military Musical Religious Slavery Southern Technological and industrial Territorial acquisitions Territorial evolution Voting rights Women.
History of Slavery in the United States. Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware Florida Georgia Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota Ohio Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Rhode Island South Carolina South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah Vermont Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming.
Slave health on plantations in the United States Treatment of slaves in the United States Slavery in the colonial United States Slavery among Native Americans in the United States Native American slave ownership.
Retrieved from " https: Slavery in the United States Slavery in the British Empire Slavery in North America. Webarchive template wayback links Pages using ISBN magic links. Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Contributions Create account Log in.
Views Read Edit View history. Navigation Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Wikipedia store. Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact page. Tools What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Wikidata item Cite this page.
This page was last edited on 15 Juneat Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License ; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Animated interactive of the history of the Atlantic slave trade.
Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Developers Cookie statement Mobile view. Contemporary Child labour Conscription Debt Forced marriage Bride buying Wife selling Forced prostitution Human trafficking Peonage Penal labour Sexual slavery.
By country or region Sub-Saharan Africa Contemporary Africa Slavery on the Barbary Coast Barbary slave trade Slave Coast Angola Chad Ethiopia Mali Mauritania Niger Somalia South Africa Sudan Seychelles North and South America Americas indigenous U. Opposition and resistance Timeline Abolitionism U. Related Common law Indentured servant Unfree labour Fugitive slaves laws Great Dismal Swamp maroons List of slaves owners Slave narrative films songs Slave name Slave catcher Slave patrol Slave Route Project Treatment in U.